Converting temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a common task, particularly for those living in places where one scale is predominantly used. In this article, we will focus on the conversion of “48 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit,” exploring the conversion process, its significance in various contexts, and the broader implications of temperature measurement in our daily lives.
The Conversion Process: How to Convert Celsius to Fahrenheit
To understand how to convert “48 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit,” it is essential to grasp the formula used for this conversion. The mathematical relationship between Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F) can be expressed with the following formula:
°F=(°C×95)+32°F = (°C \times \frac{9}{5}) + 32 °F=(°C×59)+32
Step-by-Step Conversion
Using this formula, we can convert Celsius to Fahrenheit step-by-step:
- Multiply by 9/5: Start with the Celsius temperature and multiply it by 9/5.
48×95=48×1.8=86.448 \times \frac{9}{5} = 48 \times 1.8 = 86.448×59=48×1.8=86.4 - Add 32: Next, add 32 to the result from the first step.
86.4+32=118.486.4 + 32 = 118.486.4+32=118.4
Therefore, 48 degrees Celsius is equal to 118.4 degrees Fahrenheit.
Importance of Temperature Conversion
Understanding how to convert temperatures is crucial for various reasons. Whether you are traveling, cooking, or monitoring weather patterns, the ability to switch between Celsius and Fahrenheit can enhance your comprehension and communication regarding temperature.
For instance, many countries, including the United States, primarily use Fahrenheit, while most of the world uses Celsius. This difference can lead to confusion, particularly when discussing weather forecasts, cooking recipes, or scientific experiments. Knowing how to convert temperatures accurately ensures clarity in communication and understanding.
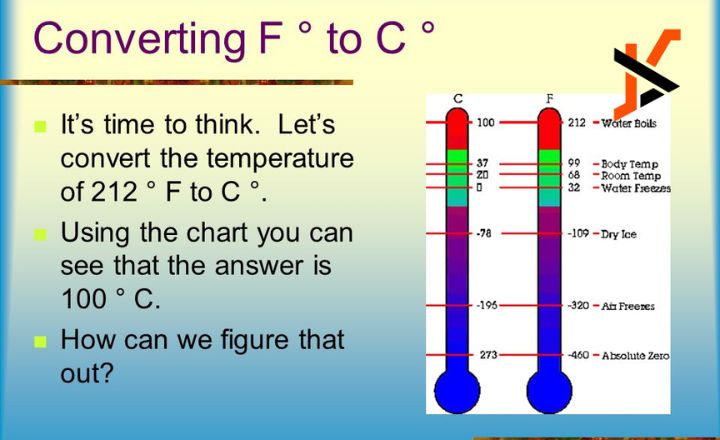
The Significance of 48 Degrees Celsius
While the process of converting “Celsius to Fahrenheit” is straightforward, it’s important to consider the implications of such a high temperature. In most contexts, 48 degrees Celsius is considered extremely hot, with various consequences for health, environment, and daily life.
Health Implications of High Temperatures
High temperatures can have serious health impacts, especially when they reach extremes like 48 degrees Celsius. Prolonged exposure to such heat can lead to heat-related illnesses, including heat exhaustion and heatstroke.
- Heat Exhaustion: Symptoms of heat exhaustion include heavy sweating, weakness, dizziness, nausea, and headache. If not addressed promptly, it can escalate into heatstroke.
- Heatstroke: This condition is a medical emergency and occurs when the body temperature rises above 40 degrees Celsius (104 degrees Fahrenheit). Symptoms include confusion, altered mental state, seizures, and loss of consciousness. Immediate medical attention is crucial to prevent serious complications or death.
Environmental Impact
High temperatures also have significant environmental implications. Regions experiencing extreme heat can face challenges such as drought, wildfires, and habitat destruction.
- Drought: Prolonged periods of high temperatures can lead to reduced rainfall and increased evaporation, creating drought conditions. This can severely affect agriculture, water supply, and local ecosystems.
- Wildfires: Extremely hot weather can contribute to the likelihood of wildfires. Dry vegetation and high temperatures create an environment conducive to fire, posing risks to both human safety and wildlife.
- Ecosystem Disruption: Many species are sensitive to temperature changes, and extreme heat can disrupt their habitats, breeding patterns, and food sources. This can lead to shifts in biodiversity and the potential extinction of vulnerable species.
Global Perspectives on Temperature Measurement
Understanding temperature conversion also involves recognizing the cultural and scientific significance of both Celsius and Fahrenheit.
Celsius: A Metric Standard
Celsius, developed by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in the 18th century, is widely used around the globe, particularly in scientific contexts. It is based on the freezing (0°C) and boiling points (100°C) of water at sea level. The Celsius scale is intuitive for many, making it easier to understand temperature changes in everyday life.
- Scientific Use: In scientific research, Celsius is the preferred scale due to its straightforward relationship with the metric system. This is particularly important in fields such as chemistry and physics, where precise temperature measurements are crucial.
- Global Adoption: Most countries use Celsius for weather reporting, cooking, and other daily temperature measurements. This widespread adoption reflects a global preference for metric systems.
Fahrenheit: An American Tradition
Fahrenheit, invented by German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, remains the standard temperature scale in the United States and a few other countries. The scale is based on a mixture of ice, water, and salt (0°F) and the average human body temperature (approximately 98.6°F).
- Cultural Context: The continued use of Fahrenheit in the U.S. is partly due to tradition and the historical development of measurement systems. Despite its practical applications, Fahrenheit can be less intuitive than Celsius since the increments are not as straightforward.
- Weather Forecasting: In the U.S., weather forecasts, cooking instructions, and other forms of communication frequently rely on Fahrenheit. This can lead to confusion for those accustomed to Celsius, especially in a globalized world.

Conclusion
The conversion of “48 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit” is not just a mathematical exercise; it represents broader themes of health, environmental impact, and cultural significance in temperature measurement. With 48 degrees Celsius equating to 118.4 degrees Fahrenheit, it is evident that such high temperatures pose serious risks to human health and the environment.
As we navigate a world increasingly affected by climate change and extreme weather events, understanding temperature conversion and its implications is more important than ever. Whether you are a traveler, a cook, or simply curious about the weather, being able to switch between Celsius and Fahrenheit can enhance your awareness and preparedness for the challenges posed by extreme temperatures.

