In recent years, technology has revolutionized various sectors, and accounting is no exception. One of the most promising advancements is the integration of augmented reality in accounting. This innovative approach enhances data visualization and improves accuracy, efficiency, and overall decision-making processes. As businesses strive to adapt to a rapidly changing environment, the adoption of augmented reality in accounting is becoming increasingly vital.
Understanding Augmented Reality
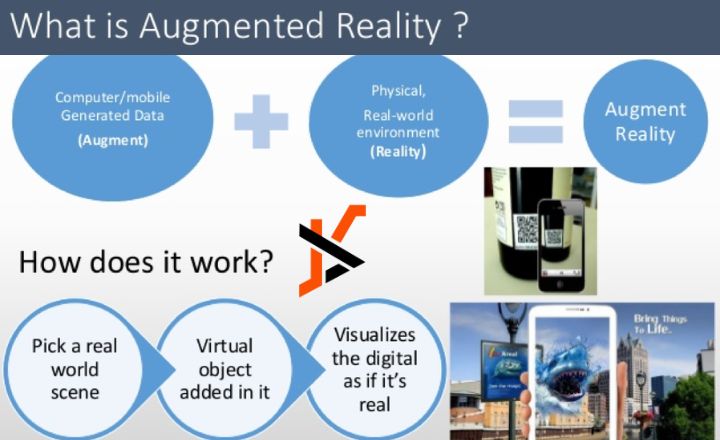
Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital information, such as images, sounds, and data, onto the real world, creating an interactive experience for users. Unlike virtual reality, which immerses users in a completely digital environment, AR enhances the real world with additional layers of information. This technology has found applications across various industries, including gaming, healthcare, and education. However, its potential in the accounting sector is just beginning to be explored.
How Augmented Reality is Shaping Accounting Practices
Enhanced Data Visualization
One of the primary benefits of augmented reality in accounting is its ability to enhance data visualization. Traditional accounting practices often rely on two-dimensional spreadsheets and reports, which can be difficult to interpret. AR allows accountants to visualize complex data sets in three dimensions, making it easier to identify trends and anomalies. For example, financial data can be represented as interactive 3D graphs that users can manipulate to explore different scenarios.
Real-Time Data Access
With augmented reality, accountants can access real-time data from anywhere. By using AR glasses or mobile devices, accountants can overlay financial information onto their physical surroundings. This capability enables professionals to make informed decisions quickly, as they can view up-to-date financial metrics while engaged in other tasks.
Improved Collaboration
Collaboration is essential in accounting, especially when teams are working remotely or across different locations. Augmented reality facilitates seamless communication by allowing multiple users to view and interact with the same data in real time. For instance, team members can gather in a virtual space, where they can analyze financial reports together, discuss findings, and brainstorm solutions as if they were in the same room.
Training and Development
The accounting profession requires continuous learning and adaptation to new technologies and regulations. Augmented reality can enhance training programs by providing immersive learning experiences. New accountants can engage with virtual simulations of real-world scenarios, allowing them to practice skills in a controlled environment. This hands-on approach leads to better retention of knowledge and prepares professionals for the challenges they will face in their careers.
Streamlined Auditing Processes
Auditing is a critical aspect of accounting that can be time-consuming and tedious. Augmented reality can streamline this process by allowing auditors to visualize and interact with financial records more effectively. For instance, auditors can use AR to overlay historical data onto current transactions, making it easier to identify discrepancies and ensure compliance with regulations. This not only saves time but also enhances the accuracy of audits.
Client Engagement
Engaging clients effectively is crucial for accounting firms. Augmented reality can enhance client interactions by offering interactive financial presentations. Instead of relying solely on traditional reports, accountants can create AR experiences that allow clients to explore their financial data in an engaging and informative way. This not only improves client understanding but also fosters stronger relationships.
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential benefits of augmented reality in accounting are significant, there are challenges to consider.

Cost of Implementation
Implementing AR technology can be costly. Businesses must invest in hardware, software, and training. Smaller firms may find it challenging to allocate resources for such advancements, potentially widening the gap between larger corporations and smaller entities.
Data Security
With the increasing reliance on digital tools, data security becomes a paramount concern. Accountants must ensure that sensitive financial information is protected when using AR applications. This includes implementing robust security measures to safeguard against data breaches.
Resistance to Change
The accounting profession has traditionally been conservative regarding technology adoption. Many professionals may be resistant to integrating augmented reality into their practices due to unfamiliarity or fear of the unknown. Overcoming this resistance requires education and clear communication about the benefits of AR.
Regulatory Compliance
As with any technological advancement in accounting, compliance with regulations is essential. Firms must ensure that the use of augmented reality aligns with industry standards and legal requirements. This may require ongoing adjustments and updates to practices as regulations evolve.
Future Trends
As augmented reality technology continues to evolve, several trends are emerging that could shape its future in accounting.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence
The integration of AR with artificial intelligence (AI) could lead to more sophisticated data analysis and predictive modeling. AI can enhance AR applications by providing tailored insights based on historical data, allowing accountants to make more informed decisions.
Mobile AR Solutions
With the increasing prevalence of smartphones and tablets, mobile AR solutions are likely to become more common in accounting. This would enable accountants to access financial data and engage with clients on the go, further enhancing flexibility and responsiveness.
Personalized Client Experiences
As AR technology matures, personalized client experiences will become more feasible. Accountants may use AR to create customized financial visualizations and reports tailored to individual client needs, improving engagement and satisfaction.

Conclusion
Augmented reality in accounting represents a significant shift in how financial professionals interact with data and clients. AR can transform the accounting landscape by enhancing data visualization, improving collaboration, and streamlining processes. However, challenges such as cost, data security, and resistance to change must be addressed to fully harness its capabilities. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of augmented reality in accounting will likely become more prevalent, paving the way for a more efficient and engaging future in the financial sector. Embracing this innovation could be the key to staying competitive in an increasingly digital world.

