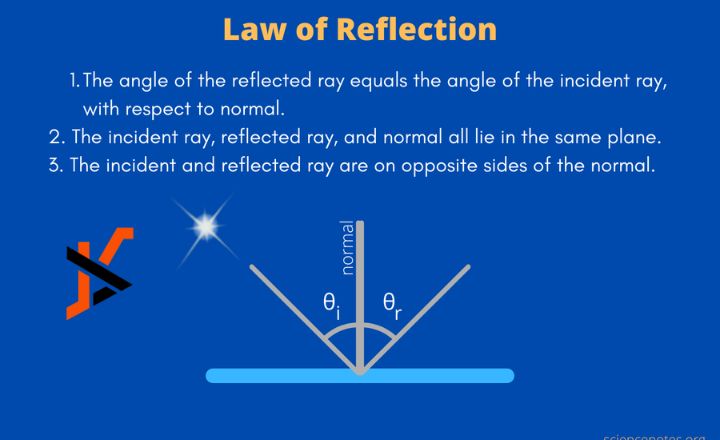
Law is a fundamental aspect of human civilization, shaping the framework within which societies operate. It governs behavior, resolves disputes, and protects individual rights, making it an indispensable component of social order. In this article, we will engage in a deep reflection about law, exploring its historical evolution, philosophical underpinnings, and its impact on contemporary society. Through this exploration, we aim to understand not only the function of law but also its complexities and the moral questions it raises.
Historical Context of Law
To truly reflect on law, we must first acknowledge its historical context. The concept of law dates back thousands of years, originating in ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Greece. Early legal codes, such as the Code of Hammurabi, established rules that governed commerce, family, and personal conduct. These codes were significant not only for their content but also for their role in introducing the idea that laws should be written and accessible to the public.
As societies evolved, so too did their legal systems. The Roman Empire contributed significantly to the development of legal principles that continue to influence modern law. Roman law introduced concepts such as equity and justice, emphasizing the importance of fairness in legal proceedings. This historical lineage shaped the foundation for many contemporary legal systems, including those based on common law and civil law traditions.
Philosophical Underpinnings of Law
Law is not just a set of rules; it is deeply intertwined with philosophy. Theories of law, known as jurisprudence, seek to answer fundamental questions about the nature of law and its purpose. Two primary schools of thought dominate legal philosophy: natural law and legal positivism.
Natural Law posits that laws are derived from moral principles inherent in human nature. Thinkers like Thomas Aquinas argued that unjust laws, which do not align with moral truths, lack legitimacy. This perspective suggests that law should reflect universal moral standards, guiding lawmakers to create just and fair legislation.
In contrast, Legal Positivism asserts that law is a man-made construct, separate from morality. According to this view, the validity of law is determined by its source rather than its moral content. Legal positivists, such as H.L.A. Hart, argue that laws are valid if they are enacted through appropriate legal processes, regardless of their ethical implications.
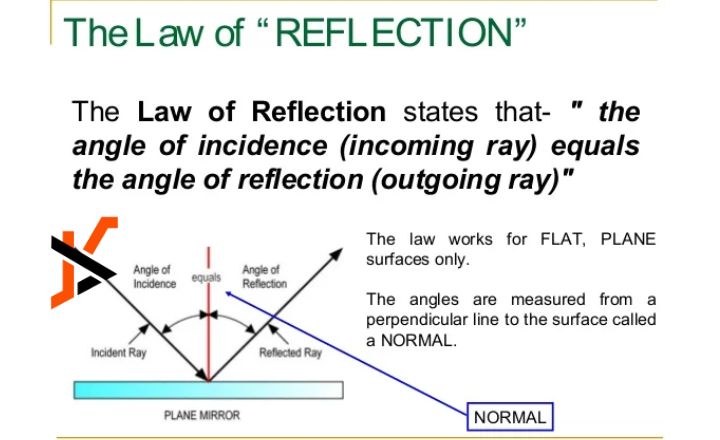
The Role of Law in Contemporary Society
In today’s world, law serves multiple functions. It acts as a tool for social control, a mechanism for conflict resolution, and a means of protecting individual rights. Understanding these roles can deepen our reflection about law and its implications.
1. Social Control
One of the primary functions of law is to maintain social order. Laws establish boundaries for acceptable behavior, deterring individuals from engaging in actions that could harm others or disrupt societal harmony. For instance, criminal laws prohibit theft, assault, and other harmful behaviors, reflecting society’s collective values about right and wrong.
However, the enforcement of laws raises important ethical questions. Who decides which behaviors are deemed criminal? Are certain laws disproportionately punitive for marginalized groups? The reflection about law must include an examination of how laws are applied and who benefits from them. Laws that perpetuate inequality or discrimination can undermine the very social order they aim to protect.
2. Conflict Resolution
Another crucial aspect of law is its role in resolving disputes. Legal systems provide mechanisms for individuals and entities to settle disagreements peacefully, whether through litigation, mediation, or arbitration. Courts serve as neutral forums where parties can present their cases and seek justice.
Yet, the efficacy of conflict resolution through law is often questioned. Legal proceedings can be lengthy, costly, and complex, often favoring those with greater resources. The concept of access to justice is vital; it raises the question of whether all individuals can equally obtain legal representation and navigate the system. Reflecting about law requires acknowledging these disparities and advocating for reforms that enhance accessibility and fairness.
3. Protection of Rights
Law also plays a pivotal role in safeguarding individual rights and liberties. Constitutional frameworks often enshrine fundamental rights, such as freedom of speech, the right to a fair trial, and protection against discrimination. These rights are essential for fostering democracy and ensuring that individuals can live free from oppression.
The enforcement of rights is not always straightforward. Governments may enact laws that infringe upon individual freedoms in the name of security or public order. For example, laws aimed at combating terrorism can sometimes lead to violations of civil liberties. Reflecting about law involves scrutinizing how laws can both protect and threaten individual rights, urging society to remain vigilant against potential abuses.
The Evolving Nature of Law
Law is not static; it evolves in response to changing societal values, technological advancements, and global challenges. The rise of digital technology has introduced new legal complexities, such as issues of privacy, cybersecurity, and intellectual property. As society grapples with these changes, legal frameworks must adapt to address emerging concerns.
Globalization has led to increased interaction among legal systems worldwide. International law has gained prominence, with treaties and agreements aimed at addressing issues such as climate change, human rights, and trade. Reflecting about law in this context requires an understanding of how local laws intersect with global norms and the challenges of harmonizing diverse legal traditions.
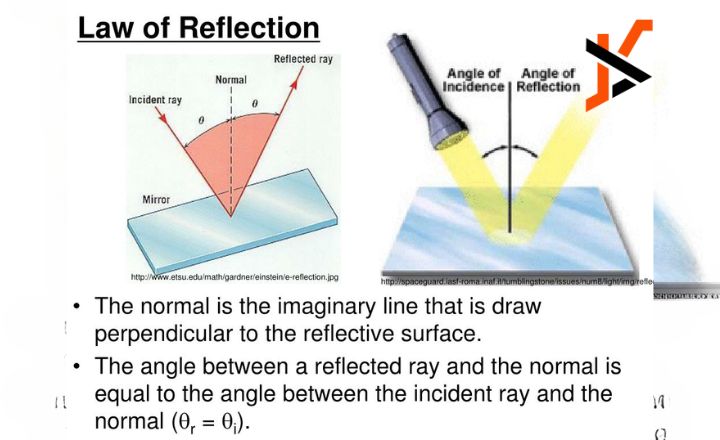
Conclusion
A thoughtful reflection about law reveals its multifaceted nature and profound impact on society. From its historical roots to its philosophical foundations, law serves as a crucial mechanism for social control, conflict resolution, and the protection of rights. However, it is essential to recognize the complexities and challenges that accompany legal systems.
As we navigate contemporary issues and global challenges, the law must evolve to remain relevant and just. Engaging in critical reflection about law encourages us to advocate for reforms that enhance fairness, accessibility, and accountability. Ultimately, a just legal system is essential for fostering a society where individuals can thrive and coexist peacefully. Through continued reflection and dialogue, we can work toward a legal framework that upholds the values of justice and equality for all.