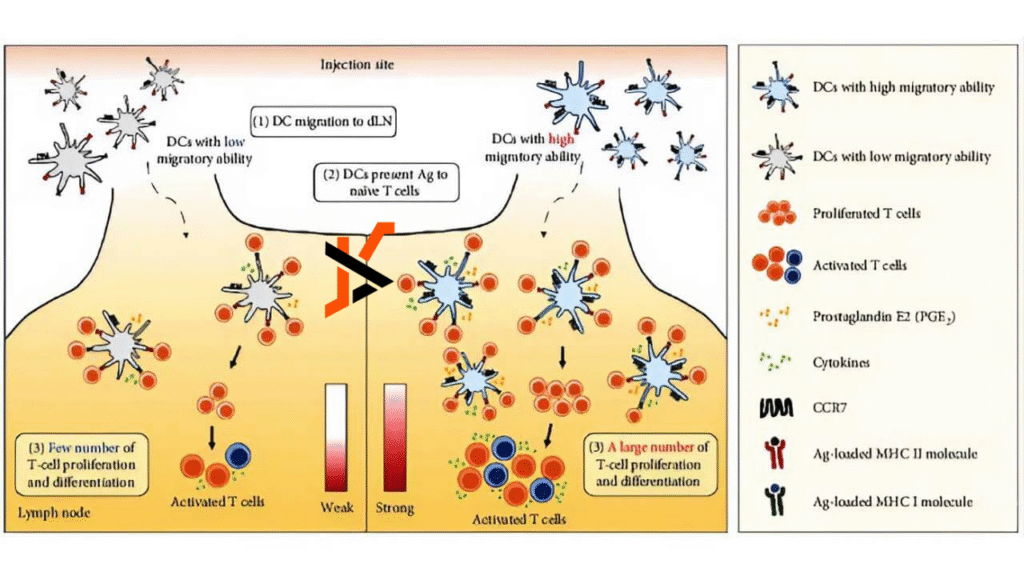
Dendritic cell immunotherapy represents one of the most advanced approaches to treating cancer by harnessing the body’s own immune system. Dendritic cells are specialized immune cells responsible for detecting foreign antigens and presenting them to T-cells, thereby initiating a targeted immune response. In cancer therapy, dendritic cells are collected from the patient, exposed to tumor-specific antigens in a laboratory, and reinfused to prime the immune system against malignant cells. Unlike traditional chemotherapy, which broadly attacks rapidly dividing cells, this immunotherapy is highly specific, minimizing collateral damage to healthy tissues.
Germany has emerged as a global leader in this field, offering patients access to highly specialized centers equipped with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) laboratories, advanced imaging, and multidisciplinary oncology teams. These centers integrate dendritic cell therapy into comprehensive treatment regimens, allowing patients with stage IV disease, where cancer has metastasized, to benefit from personalized care that combines traditional modalities with cutting-edge immunotherapy.
Applications in Stage IV Cancer
Stage IV cancer presents complex treatment challenges due to tumor spread beyond the primary site, often limiting the effectiveness of conventional therapies. Dendritic cell immunotherapy has shown promise across multiple advanced cancer types, providing immune system activation and measurable clinical benefits.
Glioblastoma and other brain cancers
Glioblastoma is one of the most aggressive brain tumors. In Germany, studies combining dendritic cell vaccination with surgery and radiochemotherapy have reported median survival extending beyond 24 months in certain patient cohorts. Immune monitoring demonstrates T-cell proliferation and tumor-specific cytotoxicity, highlighting the capacity of the therapy to enhance the immune response against residual disease.
Colorectal Cancer
In metastatic colorectal cancer, integration of dendritic cell therapy with standard systemic treatments has improved response rates and extended progression-free survival. Observational data from German centers suggest one-year survival rates exceeding 80% in select patient populations, compared to historical averages of 60–70% with conventional therapies alone. Enhanced immune responses and reduced tumor marker levels provide additional evidence of efficacy.
Pancreatic Cancer
Stage IV pancreatic cancer remains challenging, with limited therapeutic options. DC immunotherapy in Germany has been used palliatively, showing the ability to generate tumor-specific T-cell responses and stabilize disease in some patients. While overall survival gains are modest, improvements in quality of life and minimal side effects make it a valuable adjunct to palliative care.
Breast Cancer
For advanced metastatic breast cancer, dendritic cell vaccines can be combined with hormonal therapy, targeted agents, or chemotherapy to enhance tumor-specific immunity. German studies report increased antigen-specific T-cell activity and delayed disease progression, particularly in HER2-positive and triple-negative subtypes. Patients frequently experience longer periods of disease stabilization without the severe toxicity associated with conventional chemotherapy.
Melanoma (Skin Cancer)
In stage IV melanoma, DC vaccination has been used to complement checkpoint inhibitors or targeted therapies. Clinical evidence demonstrates enhanced T-cell infiltration into tumors and, in some cases, conversion of stable disease into partial or complete responses. The therapy’s low toxicity profile allows patients to maintain performance status while receiving concurrent treatments.
Lung Cancer
Patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer have benefited from dendritic cell immunotherapy by achieving measurable immune activation against tumor neoantigens. In German oncology centers, combination strategies with chemotherapy or immunotherapy have led to improved disease control rates and stabilization, offering additional treatment options when first-line therapies have failed.
Sarcoma
Stage IV sarcomas, including soft tissue and bone sarcomas, often have limited response to conventional chemotherapy. Early clinical experience in Germany indicates that dendritic cell therapy can stimulate antitumor immunity, reduce tumor progression, and, in selected cases, facilitate integration with other modalities such as surgery or targeted therapy. Immune monitoring frequently shows increased T-cell cytotoxicity and cytokine production, underscoring the therapy’s potential in this heterogeneous group of malignancies.
Clinical Outcomes and Statistics
Published clinical data indicate that dendritic cell immunotherapy is generally well-tolerated, with minimal adverse effects compared to traditional systemic therapies. Most patients experience low-grade flu-like symptoms, mild fever, or injection-site reactions. Serious adverse events are rare, and therapy-related mortality is negligible, making DC vaccines particularly attractive for patients with advanced disease who may not tolerate aggressive chemotherapy.
Survival statistics across multiple centers in Germany demonstrate meaningful benefits. In pooled analyses of DC-CIK (dendritic cell plus cytokine-induced killer cell) therapies, one-year overall survival rates have been reported at approximately 96% in intervention groups, compared with 78% in control arms. Disease stabilization often appears after several months, reflecting the time required for the immune system to mount an effective response. Importantly, durable remissions have been observed in select patients with stage IV glioblastoma, colorectal cancer, and melanoma, highlighting the potential of dendritic cell therapy to provide long-term disease control.
Advantages of Treatment in Germany
Germany offers several key advantages for patients seeking dendritic cell immunotherapy. The country’s healthcare system is renowned for its high standards, rigorous regulatory oversight, and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practice for cell-based therapies. Patients benefit from multidisciplinary care teams that integrate oncologists, immunologists, radiologists, and surgical specialists, ensuring a coordinated treatment approach. Advanced imaging and molecular diagnostics are routinely used to select optimal antigens for dendritic cell vaccines, further personalizing therapy.
Additionally, German centers often provide clinical trial access, allowing patients to receive experimental or combination therapies not available elsewhere. Treatment is typically accompanied by comprehensive follow-up monitoring, including imaging, laboratory tests, and immune system assessments, ensuring that therapy efficacy and safety are closely tracked as reported by the leading dendritic cell therapy doctor.
Patient Considerations
Dendritic cell immunotherapy is not a universal cure, and patient selection is crucial. Best outcomes are observed in patients with minimal residual disease after surgery or chemotherapy, those with well-characterized tumor antigens, and patients whose overall performance status allows them to undergo repeated immunotherapy sessions. Coordination with local healthcare providers and careful planning of travel and accommodation are essential for international patients. Platforms such as Airomedical can facilitate the connection with German oncologists, helping coordinate consultations, treatment schedules, and logistics to streamline the patient journey.
Dendritic cell immunotherapy offers a personalized, low-toxicity treatment option for patients with stage IV cancer. In Germany, specialized centers provide access to state-of-the-art laboratories, multidisciplinary teams, and clinical trial opportunities, enabling patients to benefit from cutting-edge immunotherapy in combination with conventional modalities. Clinical outcomes demonstrate improved survival and immune activation across multiple tumor types, from glioblastoma to metastatic colorectal and pancreatic cancers. While not universally curative, dendritic cell therapy represents a promising strategy for extending life, enhancing quality of life, and providing hope for patients with advanced cancer.