From Bottlenecks to Breakthrough: Why CRISPR Knock-In Matters
Across research labs, many scientists still spend months trying to insert a single gene, only to end up with unpredictable clones. Long screening cycles, off-target effects and rising costs have turned precise cell-line editing into a stubborn bottleneck.
Over the past few years, CRISPR knock-in has started to change that picture. By pairing Cas9 with thoughtfully designed guide RNAs and donor templates, researchers can insert or modify genes at defined locations, often shortening timelines dramatically and gaining greater confidence in their models. This article explains how the knock-in process works, what makes it efficient and practical tips for applying it in your own projects. For a full protocol and step-by-step guide to performing CRISPR knock in, check out this resource.

Now that we’ve seen why it matters, let’s look at how it works.
How CRISPR Knock-In Works Within the Broader CRISPR Gene Editing Framework
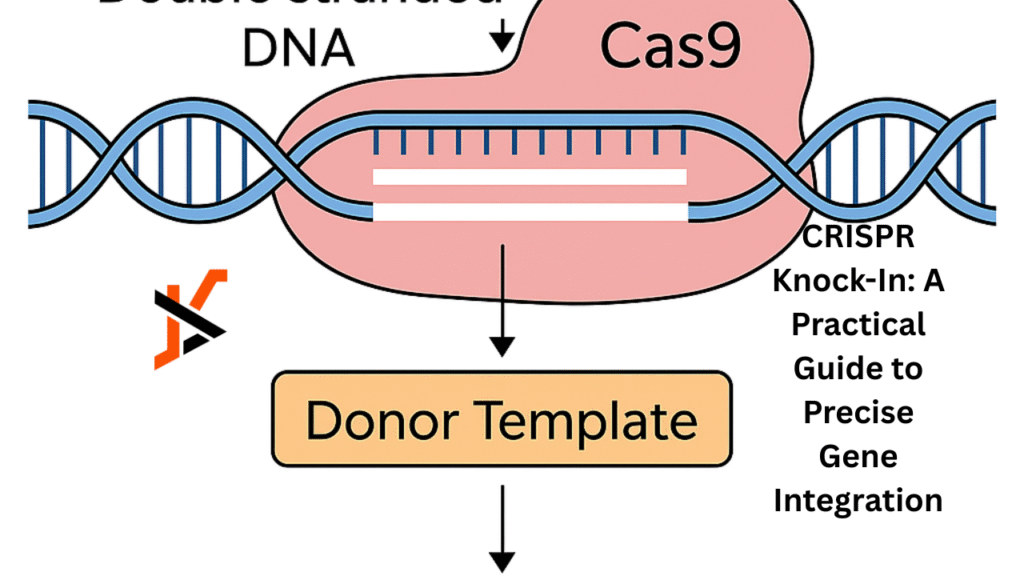
At its heart, CRISPR knock-in uses the Cas9 nuclease guided by a custom RNA sequence to make a precise cut at the chosen genomic location. When a donor DNA template is supplied at the same time, the cell’s own homology-directed repair machinery can seamlessly integrate new genetic material exactly where it’s needed.
This strategy enables researchers to add fluorescent tags, correct disease-causing mutations or insert functional elements with far greater accuracy than older techniques. Understanding this mechanism is essential for designing efficient experiments and avoiding wasted time or off-target edits. To explore the entire range of CRISPR gene editing applications and see how the technology can advance your projects, click here.
With the basics of CRISPR gene editing in mind, here’s how to plan a knock-in experiment.
Designing for Success: The CRISPR Knock-In Workflow

Planning ahead is half the battle. In practice, a knock-in experiment unfolds in three interconnected stages: design, delivery and validation. Thinking through each stage up front dramatically improves success rates.
Design Phase
- Select the target site and design sgRNAs carefully. Choose sequences with low off-target potential and accessible PAM sites to maximize specificity.
- Construct the donor template. Decide between single-stranded or double-stranded donors; include homology arms, tags or reporters to simplify downstream screening.
Delivery Phase
- Choose the optimal delivery system. Plasmid transfection, electroporation of RNP complexes or viral vectors may work best depending on your cell type.
- Optimize cell cycle timing. Synchronizing cells in S/G2 phase can boost homology-directed repair efficiency.
Validation Phase
- Screen for correct integration. Use PCR, sequencing or functional assays to confirm edits quickly.
- Expand verified clones. Maintain low passage numbers and good cell health to preserve genotype.
Once design and delivery are complete, rigorous validation ensures you’re working with the correct edits before scaling up your experiments.
Troubleshooting Common Pitfalls in CRISPR Knock-In
Even well-planned knock-in experiments can hit roadblocks. Knowing the most common issues — and how others have solved them — saves time and frustration.
Low HDR Efficiency
A frequent snag is low homology-directed repair rates, which leave few correctly edited clones. Labs often improve efficiency by extending the length of homology arms, synchronizing cells in S/G2 phase or delivering CRISPR components as ribonucleoprotein complexes to shorten exposure time.
Off-Target Effects
Cas9 can sometimes cut unintended sites, introducing unwanted mutations. High-fidelity Cas9 variants, careful sgRNA design with stringent off-target scoring and early verification with targeted sequencing help protect data integrity.
Cell-Type Variability
Some cell lines are notoriously difficult to transfect or repair. Testing multiple delivery methods, optimizing culture conditions and working with low-passage, authenticated cells can improve responsiveness and raise success rates.
Screening Bottlenecks
Long screening cycles slow projects and inflate costs. Incorporating selectable markers or reporter systems into donor templates allows quick identification of correct integrants and cuts the number of clones to verify.
Real-World Impact: Where CRISPR Knock-In Delivers

Beyond solving technical challenges, CRISPR knock-in creates tangible benefits across several research areas.
Disease Modeling
What it does: Introduce or correct precise mutations in cell lines to mimic human genetic conditions.
Why it matters: Highly accurate in-vitro models let scientists study disease mechanisms and test therapies while reducing reliance on animal testing.
Cell Therapy Engineering
What it does: Insert therapeutic genes or safety switches into immune cells such as T cells or NK cells.
Why it matters: Enables creation of more potent, controllable cell therapies for cancer and other diseases.
Functional Genomics
What it does: Tag endogenous proteins with reporters or functional domains to study their role in real time.
Why it matters: Provides cleaner data than overexpression systems and speeds up pathway analysis.
Translational Research
What it does: Build knock-in animal models or patient-derived cell lines with specific edits.
Why it matters: Bridges the gap between basic research and preclinical studies, increasing confidence that results will translate to the clinic.
These examples show how knock-in moves from theory to real-world impact.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Precise Gene Integration
CRISPR knock-in has already changed genome engineering, but the next wave of innovation is on the horizon.
Prime Editing and Beyond
What it is: A newer approach that combines CRISPR with a reverse transcriptase to “write” new genetic information without creating double-strand breaks.
Why it matters: Offers a way to introduce complex edits with fewer off-target effects, potentially complementing or replacing traditional knock-in for certain applications.
Base Editing Refinements
What it is: Tools that directly convert one DNA base into another without double-strand breaks.
Why it matters: While not a knock-in per se, base editing achieves single-nucleotide changes previously possible only via labor-intensive HDR.
AI-Driven Design and Automation
What it is: Machine learning models that predict the most efficient sgRNAs, donor templates and delivery conditions, paired with robotic platforms to execute experiments.
Why it matters: Could dramatically raise success rates and reduce trial-and-error, lowering costs and speeding up high-throughput projects.
Improved Delivery Systems
What it is: New viral and non-viral vectors that boost editing efficiency or target previously hard-to-reach cell types.
Why it matters: Expands the range of cells and organisms where precise knock-ins are practical, from primary human cells to non-model species.
Mastering knock-in today sets you up for these advances tomorrow.
Conclusion
CRISPR knock-in has evolved from an experimental technique into a core method for building accurate cell and animal models, inserting functional elements and correcting disease-relevant mutations. By understanding how the process works, planning each step carefully and applying proven troubleshooting strategies, researchers can markedly improve their editing efficiency and confidence in the results.
As the technology matures, its integration with emerging tools such as prime editing, base editing and AI-driven design promises even greater precision and accessibility. For scientists at the frontiers of genomics, mastering CRISPR knock-in today lays the groundwork for faster discoveries and more reliable translational research tomorrow.