Introduction
In the digital age, the sheer volume of data generated daily is staggering. The data landscape is expanding exponentially from social media interactions to e-commerce transactions. With this explosion of data, traditional data retrieval and analysis methods are struggling to keep pace. Enter vector search and vector databases, innovative technologies that revolutionise how we interact with and extract insights from vast datasets.
Understanding Vector Search
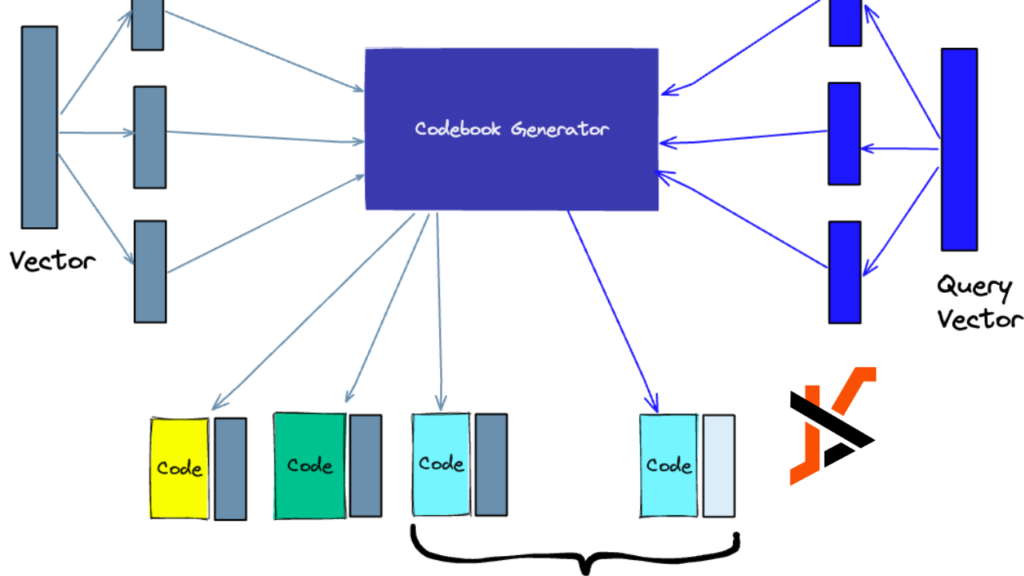
Vector search is a cutting-edge approach to information retrieval that leverages mathematical vectors to represent data points in a high-dimensional space. Unlike traditional keyword-based searches, which rely on exact matches, vector search considers data’s semantic meaning and context, enabling more accurate and nuanced results.
How Vector Search Works
- Vectorization: Data points are converted into numerical vectors using word embeddings or deep learning models.
- High-Dimensional Space: These vectors are then plotted in a high-dimensional space, where each dimension represents a unique feature or characteristic.
- Similarity Matching: Queries are also vectorized and compared to the existing vectors in the space to identify the most similar data points.
Advantages of Vector Search
- Semantic Understanding: Vector search captures the semantic relationships between data points, allowing for more contextually relevant results.
- Scalability: It is highly scalable and can handle massive datasets with millions or even billions of data points.
- Flexibility: Vector search is adaptable to various data types, including text, images, and audio.
The Emergence of Vector Databases
As the demand for more efficient and intelligent data retrieval grows, traditional relational databases face limitations in handling modern datasets’ complexity and scale. Vector databases offer a compelling alternative by combining the principles of vector search with the functionality of a database management system.
Key Features of Vector Databases
- Vector Storage: Data is stored in vectorized form, allowing for efficient similarity searches and analytics.
- Real-Time Processing: Vector databases support real-time querying and analysis, enabling rapid insights into dynamic datasets.
- Anomaly Detection: These databases can detect anomalies and patterns within data streams by analysing vector similarities.
- Integration with ML: Vector databases seamlessly integrate with machine learning workflows, facilitating model training and inference on large-scale datasets.
Applications of Vector Databases
- Recommendation Systems: E-commerce platforms use vector databases to power personalized recommendations based on user preferences and behaviours.
- Fraud Detection: Financial institutions leverage vector databases to detect fraudulent activities by identifying unusual patterns in transaction data.
- Content Similarity: Media companies utilize vector databases to recommend similar articles, videos, or music based on content similarity.
Challenges and Considerations
While vector search and vector databases offer promising solutions to the challenges of modern data retrieval, they are not without their complexities and considerations.
Computational Complexity
Performing similarity searches in high-dimensional vector spaces can be computationally intensive, requiring efficient algorithms and hardware optimizations.
Data Quality and Representation
The accuracy and relevance of vector representations depend heavily on the quality and diversity of the underlying data and the chosen vectorization techniques.
Privacy and Security
As with any data-driven technology, ensuring the privacy and security of sensitive information remains a critical concern, particularly in industries like healthcare and finance.
Future Directions
As the adoption of vector search and databases grows, ongoing research and development focus on addressing existing challenges and unlocking new possibilities.
Enhanced Efficiency
Efforts are underway to optimize algorithms and hardware architectures to improve the efficiency and scalability of vector-based retrieval systems.
Interdisciplinary Applications
Vector search techniques are being applied across diverse domains, from natural language processing to bioinformatics, opening up new avenues for innovation and discovery.
Ethical Considerations
As with any transformative technology, the ethical implications of widespread adoption, including bias, fairness, and accountability, must be considered.
Conclusion
Vector search and vector databases represent a paradigm shift in approaching data retrieval and analysis. By harnessing the power of high-dimensional vector spaces, these technologies offer unparalleled accuracy, scalability, and flexibility in navigating the vast seas of data in the digital age. As we continue to explore the potential of these innovations, it is imperative to remain vigilant in addressing challenges and ensuring that they are harnessed responsibly for the benefit of society.