Introduction to SQL Server DBA Support
SQL Server DBA support is more than just keeping the lights on. It’s about ensuring data is available, secure, and performing well. Think of it as the backbone of any data-driven organization.
It involves a mix of proactive tasks and reactive problem-solving. A good DBA anticipates issues before they arise, but also knows how to quickly fix things when they break. This is where solid sql server dba support comes in.
Effective DBA support is critical for business continuity. Without it, companies risk data loss, security breaches, and performance bottlenecks. These can all lead to significant financial and reputational damage.
Understanding SQL Server Management
SQL Server management is more than just keeping the lights on. It’s about ensuring data is available, secure, and performing well. Think of it as the backbone of any data-driven application.
Effective SQL Server management involves a mix of proactive tasks and reactive responses. It’s about planning for the future while also addressing immediate needs. A good DBA is always learning and adapting.
It’s a continuous cycle of monitoring, tuning, and securing. Neglecting any of these areas can lead to serious problems down the road. Proper SQL Server management is key to success.
Neglecting Regular Backups
Backups are your safety net. Without them, data loss can be catastrophic. Imagine losing years of critical business data. Not a good look.
It’s not enough to just have backups. You need to test them regularly. Make sure you can actually restore your data when needed. Schedule regular tests.
Think of backups as insurance. You hope you never need them, but you’re sure glad you have them when disaster strikes. Don’t skip this step.
Ignoring Performance Monitoring
Performance monitoring is like a health check for your SQL Server. It helps you identify bottlenecks and potential problems before they cause major issues. It’s a must.
Ignoring performance metrics is like driving a car without looking at the dashboard. You might be fine for a while, but eventually, something will break. Be proactive.
Tools like SQL Server Profiler and Performance Monitor can provide valuable insights. Use them to track key metrics like CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk I/O.
Failing to Optimize Queries
Slow queries can kill performance. Unoptimized queries waste resources and frustrate users. It’s like trying to run a marathon in flip-flops. Not efficient.
Query optimization involves analyzing query execution plans and identifying areas for improvement. Indexing, rewriting queries, and updating statistics can all help.
Consider using tools like the Database Engine Tuning Advisor. It can provide recommendations for optimizing queries and improving overall performance.
Overlooking Security Best Practices
Security is paramount. A data breach can be devastating. It can damage your reputation and cost you money. Don’t take it lightly.
Overlooking security best practices is like leaving your front door unlocked. It invites trouble. Implement strong passwords, restrict access, and encrypt sensitive data.
Stay up-to-date on the latest security threats and vulnerabilities. Patch your SQL Server regularly and monitor for suspicious activity. Security is an ongoing process.
Common Mistakes in SQL Management
It’s easy to make mistakes when managing SQL servers. These errors can lead to performance issues, data loss, or even security breaches. Knowing what to avoid is half the battle. Let’s look at some common pitfalls in SQL management.
Neglecting Regular Backups
Not backing up your database is like not having insurance. It’s a disaster waiting to happen. If something goes wrong, you’ll lose everything. Backups should be automated and tested regularly.
- Schedule daily backups.
- Store backups offsite.
- Test your restore process.
Without backups, a server crash or data corruption can be fatal. Regular backups are the safety net that every DBA needs.
Ignoring Performance Monitoring
Ignoring performance is like driving a car without looking at the dashboard. You might be okay for a while, but eventually, something will break. Monitoring helps you identify bottlenecks and optimize your SQL management.
- Track CPU usage.
- Monitor disk I/O.
- Analyze query performance.
Failing to Optimize Queries
Slow queries can bring your entire system to a crawl. It’s important to write efficient SQL code. Indexing, query tuning, and avoiding full table scans are key.
- Use indexes wisely.
- Rewrite slow queries.
- Analyze execution plans.
Overlooking Security Best Practices
Security should be a top priority. Weak passwords, unpatched systems, and lack of access controls can leave you vulnerable. Implement a strong security posture to protect your data. It’s not just about preventing attacks; it’s about building trust.
- Use strong passwords.
- Apply security patches.
- Restrict user permissions.
Best Practices for SQL Server Management

SQL Server management requires a proactive approach. It’s not just about keeping the lights on. It’s about ensuring optimal performance, security, and reliability. Let’s look at some key best practices.
Implementing a Backup Strategy
Backups are your safety net. A solid backup strategy is non-negotiable. Without it, you risk losing everything. It’s that simple.
- Regularly back up your databases. This includes full, differential, and transaction log backups. Tailor the frequency to your recovery point objective (RPO).
- Test your backups. Don’t just assume they work. Restore them to a test environment to verify their integrity.
- Store backups securely. Consider offsite storage or cloud-based solutions for disaster recovery.
Backups are more than just copies of your data; they are your insurance policy against data loss. Treat them with the respect they deserve.
Utilizing Performance Monitoring Tools
Performance monitoring is key to a healthy SQL Server environment. You can’t fix what you can’t see. So, get visibility into your server’s performance.
- Use SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). It offers basic monitoring capabilities.
- Consider third-party tools. Products like SolarWinds or Red Gate SQL Monitor provide advanced features.
- Set up alerts. Get notified when key metrics exceed thresholds. This allows for proactive intervention.
Regularly Updating and Patching SQL Server
Keeping your SQL Server up-to-date is crucial. Updates and patches address security vulnerabilities. They also improve performance and stability.
- Stay informed about new releases. Microsoft regularly releases updates and service packs.
- Test patches in a non-production environment first. This minimizes the risk of introducing new issues.
- Automate the patching process. Use tools like Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) to streamline updates. This ensures consistent SQL Server management.
Conclusion: Enhancing SQL Server DBA Support

SQL Server DBA support is a continuous journey, not a destination. It’s about constantly learning, adapting, and refining your strategies. The goal? A robust, secure, and efficient database environment.
Effective SQL Server DBA support means more than just fixing problems. It involves proactive planning, diligent monitoring, and a commitment to best practices. This approach minimizes downtime and maximizes performance.
By avoiding common pitfalls and embracing proactive strategies, organizations can significantly improve their SQL Server environments. This leads to better performance, enhanced security, and reduced risk.
Ultimately, strong SQL Server DBA support translates to better business outcomes. It ensures that data, the lifeblood of modern organizations, is always available, reliable, and secure.
Wrapping It Up
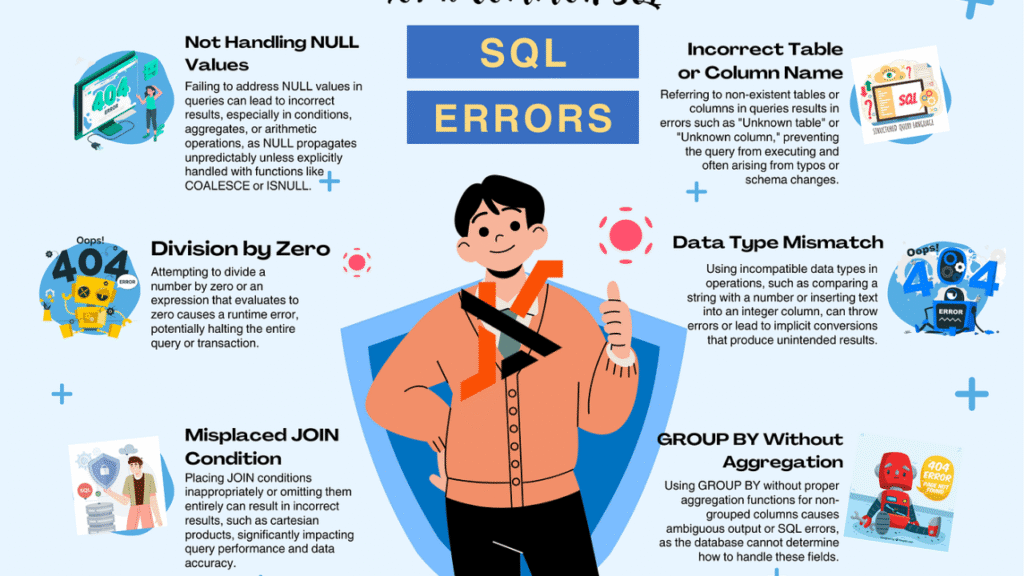
In summary, avoiding these common SQL mistakes can really boost how well your database applications run. By tweaking your queries, steering clear of nested views, breaking up big multi-table tasks, picking the right clustering keys, using smart data checks, opting for stored procedures instead of triggers, and fine-tuning negative searches, you can make your SQL code work better. Knowing these common pitfalls and sticking to best practices will help your database handle more data smoothly, especially as it grows. Remember, everyone makes mistakes, but learning from them is what counts.